Photos and X-rays on endodontic access means root canal opening into pulp created in our Root Canal office. Please visit this link for more info on endodontic therapy.
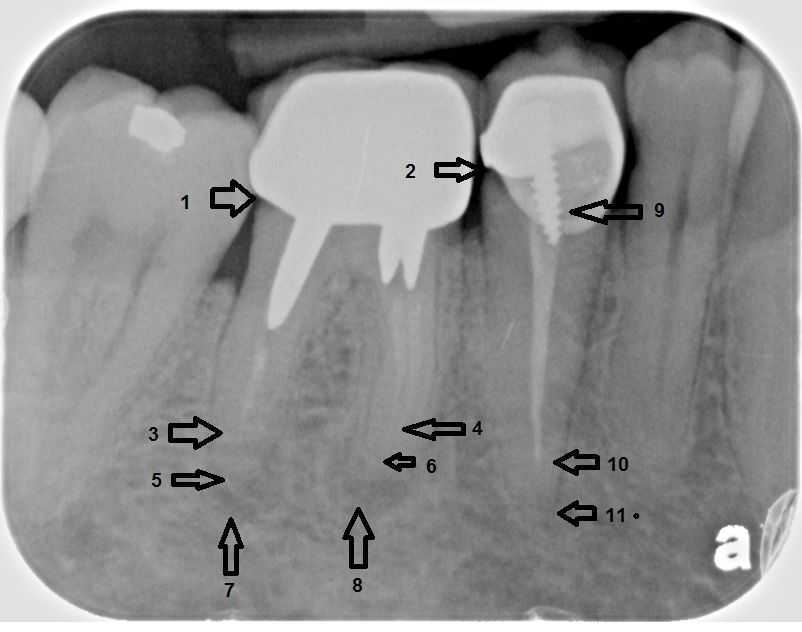
The root canal filling (arrows 3, 4 & 10) does not extend to the end of the tooth root (arrows 5, 6 & 11). 7) & 8) Radiographic evidence of an active root canal infection in the jaw. Pain in this tooth was the reason for this new patient visit. 9) A poor-fitting prefabricated post. The molar tooth will likely need extraction and replacement with a dental implant and new crown because the three posts appear to block access to all three canals. The premolar tooth will need root canal retreatment, a new post, possible gum surgery and a new crown.
Endodontics root canal access tooth opening.
1. X-ray shows periapical pathology – root canal infection – in tooth #29. This new patient had chronic tooth pain following her original root canal therapy. 2. The endodontist found a second root canal with endodontic files. 3. X-ray of a file in the second canal. 4. Post preparation in the second canal of tooth #29 after obturation with gutta percha. During root canal treatment – endodontics – the Endodontist needs to confirm that he/she is cleaning and shaping the tooth root canal to the full length of the tooth. The result should not be longer or shorter than the length of the tooth. The Endodontist will frequently use an electronic tooth root apex locator in conjunction with dental xrays radiographs to confirm this measurement. The Endodontist will always want a pre-treatment x-ray to help radiographic diagnosis and a final treatment x-ray to confirm that the root canal filling – endodontic obturation – is at the correct length within the root canal space.
1. X-ray shows periapical pathology – root canal infection – in tooth #29. This new patient had chronic tooth pain following her original root canal therapy. 2. The endodontist found a second root canal with endodontic files. 3. X-ray of a file in the second canal. 4. Post preparation in the second canal of tooth #29 after obturation with gutta percha. During root canal treatment – endodontics – the Endodontist needs to confirm that he/she is cleaning and shaping the tooth root canal to the full length of the tooth. The result should not be longer or shorter than the length of the tooth. The Endodontist will frequently use an electronic tooth root apex locator in conjunction with dental xrays radiographs to confirm this measurement. The Endodontist will always want a pre-treatment x-ray to help radiographic diagnosis and a final treatment x-ray to confirm that the root canal filling – endodontic obturation – is at the correct length within the root canal space.
Endodontic therapy access tooth opening.
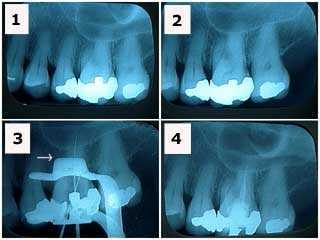
1) & 2) X-rays of tooth #14 showing a large, old silver filling in a patient who had been experiencing tooth pain. Note the decreased size of the pulp chamber in this tooth making access to the root canals more difficult. 3) X-ray of endodontic file lengths. Note that the calcification in the mesial root of #14 initially prevented instrumentation. 4) Final endodontic obturation showing that the mesial root of #14 was located and treated. Chronic inflammation in the dental pulp due to the presence of large, old fillings can increase the difficulty of root canal access. Earlier root canal therapy should be considered in these situations.
1) & 2) X-rays of tooth #14 showing a large, old silver filling in a patient who had been experiencing tooth pain. Note the decreased size of the pulp chamber in this tooth making access to the root canals more difficult. 3) X-ray of endodontic file lengths. Note that the calcification in the mesial root of #14 initially prevented instrumentation. 4) Final endodontic obturation showing that the mesial root of #14 was located and treated. Chronic inflammation in the dental pulp due to the presence of large, old fillings can increase the difficulty of root canal access. Earlier root canal therapy should be considered in these situations.
Endodontics root canal access tooth opening.
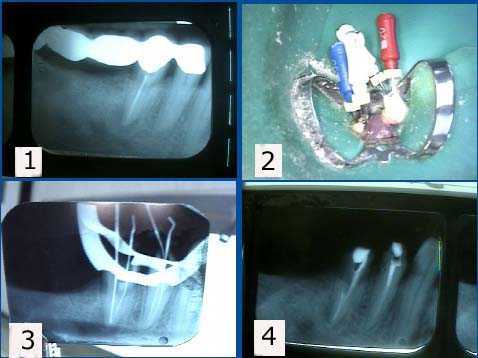
1) Root canal access attained and showing the distal and two mesial root canals. 2) Lateral condensation of the distal root canal after the master cone with root canal cement was placed. 3) The auxillary point is placed in the distal canal after the root canal spreader was removed. 4) All three canals are obturated with gutta percha. A cotton pellet and Cavit will be placed as a temporary dental filling.
1) Root canal access attained and showing the distal and two mesial root canals. 2) Lateral condensation of the distal root canal after the master cone with root canal cement was placed. 3) The auxillary point is placed in the distal canal after the root canal spreader was removed. 4) All three canals are obturated with gutta percha. A cotton pellet and Cavit will be placed as a temporary dental filling.
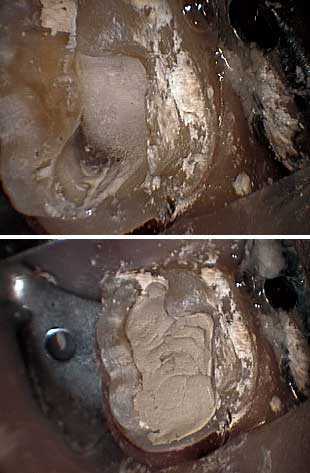
Endodontics therapy access tooth opening.
Cotton is placed in the root canal access to facilitate the location of the root canals during the subsequent dental procedures. Cavit is placed as a temporary dental filling.
Cotton is placed in the root canal access to facilitate the location of the root canals during the subsequent dental procedures. Cavit is placed as a temporary dental filling.
Endodontics root canal access tooth opening.
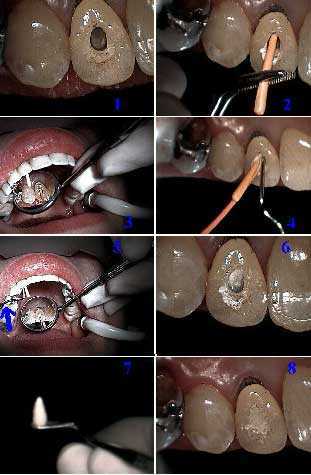
How to root canal technique for an upper right lateral incisor tooth through a dental crown. Photo 1) Access is prepared through the tooth crown. Photos 2) & 3) Placement of the primary gutta percha point. Photos 4) & 5) Condensation of the accessory gutta percha points. Photos 6) & 7) Heating the endodontic condenser to vertically condense and cut the gutta percha at the pulpal chamber floor. Photo 8) Placement of the temporary filling.
How to root canal technique for an upper right lateral incisor tooth through a dental crown. Photo 1) Access is prepared through the tooth crown. Photos 2) & 3) Placement of the primary gutta percha point. Photos 4) & 5) Condensation of the accessory gutta percha points. Photos 6) & 7) Heating the endodontic condenser to vertically condense and cut the gutta percha at the pulpal chamber floor. Photo 8) Placement of the temporary filling.

Endodontics therapy access tooth opening. This picture shows the initial endodontic access through a large silver filling. Access is the first step in endodontic therapy.
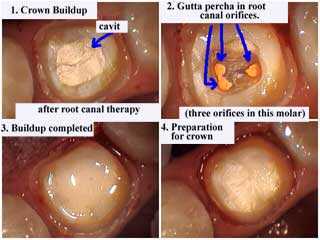
Endodontics root canal access tooth opening. The upper right photo shows the root canal access with gutta percha – orange color – seen in the root canal orifices of the pulp chamber floor. Crown buildup after root canal therapy. Then preparation for a crown.
Endodontic therapy access teeth opening.
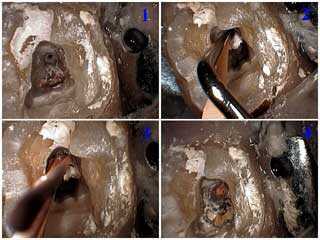
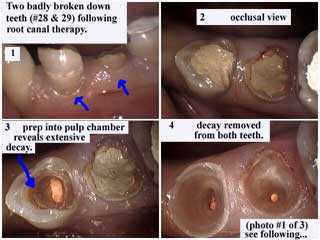
Two lower premolar teeth with very bad tooth decay following root canal therapy. The occlusal view first shows the temporary filling in place and then the initial root canal access preparation into the pulp chamber reveals extensive tooth decay. The final photo shows teeth decay removed from both teeth.
Two lower premolar teeth with very bad tooth decay following root canal therapy. The occlusal view first shows the temporary filling in place and then the initial root canal access preparation into the pulp chamber reveals extensive tooth decay. The final photo shows teeth decay removed from both teeth.
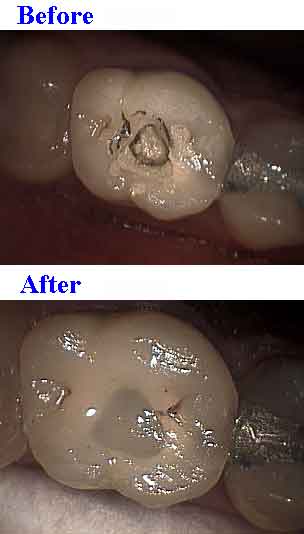
Endodontics root canal access tooth opening.
Dental bonding to seal endodontic access through a porcelain tooth crown. Porcelain etch and silane prime the width of porcelain exposed through the root canal access in addition to all other bonding steps. This will minimize subsequent microleakage.
Dental bonding to seal endodontic access through a porcelain tooth crown. Porcelain etch and silane prime the width of porcelain exposed through the root canal access in addition to all other bonding steps. This will minimize subsequent microleakage.