Before and after photos on root canal infection causes pain swelling and abscess performed in our Root Canal office. Infection that leads to a swollen jaw can become life-threatening and needs immediate medical attention.
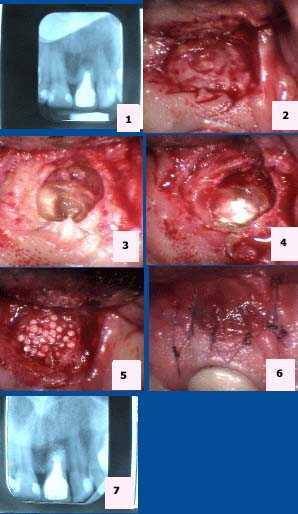
Pictures show how to treat endodontics root canal failure. Apicoectomy is root canal oral surgery that is needed when traditional root canal therapy has failed and cannot be retreated through the root canal of the dental crown.
Apicoectomy tooth #9. 1) Pre-op x-ray. 2) Isolation of the apical area. 3) Exposure of the tooth root apex. 4) Placement of MTA (mineral trioxide aggregate). 5) Placement of Bioplant HTR (hard tissue replacement). 6) 6-0 Vicryl sutures. 7) Post-op x-ray.
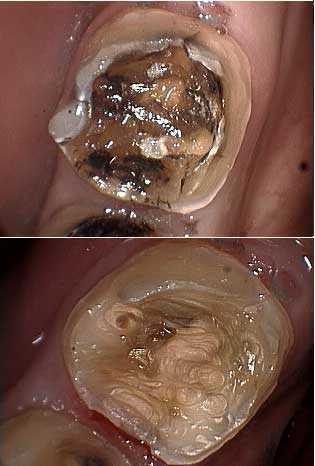
Endodontics root canal problems complications. A lower molar tooth after removal of dental caries. The patient had experienced severe tooth and jaw pain in this area. Vitality testing by the endodontist showed it was non vital and the x-ray showed calcification in the root canal.
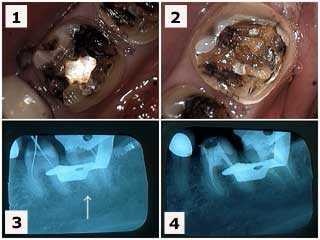
Endodontics root canal problems complications associated with a swollen jaw.
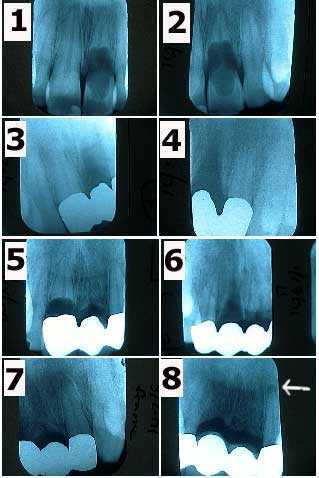
1) & 2) Two lower left molars in a new patient who had complained of severe jaw and teeth pain. These pictures show the molars after removal of large, old silver dental fillings. 3) X-ray of the endodontic file lengths. Note that the calcification in the mesial root of #18 initially prevented instrumentation by the endodontist. 4) Final endodontic obturation showing that the mesial root of #18 was located and treated. Chronic inflammation in the dental pulp due to the presence of large, old dental fillings can increase the difficulty of performing root canal because of calcification. Earlier root canal therapy should be considered in these situations.
1) & 2) Two lower left molars in a new patient who had complained of severe jaw and teeth pain. These pictures show the molars after removal of large, old silver dental fillings. 3) X-ray of the endodontic file lengths. Note that the calcification in the mesial root of #18 initially prevented instrumentation by the endodontist. 4) Final endodontic obturation showing that the mesial root of #18 was located and treated. Chronic inflammation in the dental pulp due to the presence of large, old dental fillings can increase the difficulty of performing root canal because of calcification. Earlier root canal therapy should be considered in these situations.
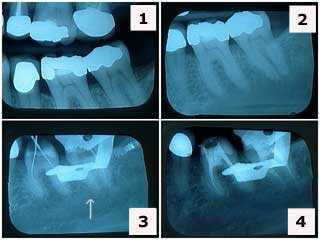
Endodontics root canal problems complications.
1) & 2) X-rays of tooth #’s 19 & 18 showing large, old silver dental fillings in a 38 year-old female patient who had been experiencing teeth pain. Note the decreased size of the pulp chambers in these teeth. 3) X-ray of endodontic file lengths. Note that the calcification in the mesial root of #18 initially prevented instrumentation. 4) Final endodontic obturation showing that the mesial root of #18 was located and treated. Chronic inflammation in the dental pulp due to the presence of large, old fillings can increase the difficulty of root canal therapy. Performing root canal therapy sooner should be considered in these situations.
1) & 2) X-rays of tooth #’s 19 & 18 showing large, old silver dental fillings in a 38 year-old female patient who had been experiencing teeth pain. Note the decreased size of the pulp chambers in these teeth. 3) X-ray of endodontic file lengths. Note that the calcification in the mesial root of #18 initially prevented instrumentation. 4) Final endodontic obturation showing that the mesial root of #18 was located and treated. Chronic inflammation in the dental pulp due to the presence of large, old fillings can increase the difficulty of root canal therapy. Performing root canal therapy sooner should be considered in these situations.
Endodontics root canal problems complications.
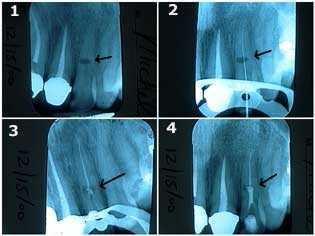
An extreme case of internal resorption occurring within several teeth of a 30 year-old male over ten years. 1) & 2) The patient related a history of trauma to the upper anterior teeth when these x-rays were taken in 1/91. Tooth #9 is exhibiting severe internal resorption. 3) & 4) X-rays of the framework of a three tooth dental bridge in 3/91 following extraction of tooth #9. 5) Tooth #8 exhibiting severe internal resorption in 5/93. 6) & 7) X-rays of the framework of a four tooth dental bridge in 7/93 following extraction of tooth #8. 8) X-rays of the tooth dental bridge abutments #7 & 10 in 4/00 shows a periapical radiolucency appearing around #10. The patient was informed of the need for root canal therapy. X-rays in 5/95 & 12/97 had not showed pathologic changes.
An extreme case of internal resorption occurring within several teeth of a 30 year-old male over ten years. 1) & 2) The patient related a history of trauma to the upper anterior teeth when these x-rays were taken in 1/91. Tooth #9 is exhibiting severe internal resorption. 3) & 4) X-rays of the framework of a three tooth dental bridge in 3/91 following extraction of tooth #9. 5) Tooth #8 exhibiting severe internal resorption in 5/93. 6) & 7) X-rays of the framework of a four tooth dental bridge in 7/93 following extraction of tooth #8. 8) X-rays of the tooth dental bridge abutments #7 & 10 in 4/00 shows a periapical radiolucency appearing around #10. The patient was informed of the need for root canal therapy. X-rays in 5/95 & 12/97 had not showed pathologic changes.
Endodontics root canal problems complications.
Treatment of internal resorption in an upper left lateral incisor tooth. This 40-year-old female related a history of trauma to her front teeth during a horseback riding accident. 1) The oval-shaped radiolucency in the middle of the tooth length is the site of the internal resorption. The patient was informed of the guarded long-term prognosis of the tooth. 2) & 3) Traditional root canal therapy was first performed. The canal space was cleaned and shaped, sterilized with NaOCL, and then filled with gutta percha up to a point apical to the internal resorption. 4) MTA, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, was then placed into the area of the internal resorption and coronal to it. Keeping the MTA moist will give more working time for condensation of material.
Treatment of internal resorption in an upper left lateral incisor tooth. This 40-year-old female related a history of trauma to her front teeth during a horseback riding accident. 1) The oval-shaped radiolucency in the middle of the tooth length is the site of the internal resorption. The patient was informed of the guarded long-term prognosis of the tooth. 2) & 3) Traditional root canal therapy was first performed. The canal space was cleaned and shaped, sterilized with NaOCL, and then filled with gutta percha up to a point apical to the internal resorption. 4) MTA, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate, was then placed into the area of the internal resorption and coronal to it. Keeping the MTA moist will give more working time for condensation of material.
Endodontics root canal failure leading to tooth extraction. The top x-ray shows a very large periapical radiolucency consistent with periapical pathology around both tooth root apices of this lower first molar. The jaw was swollen.
Endodontics root canal failure leading to tooth extraction. Extraction of tooth #30 due to severe periapical pathology. 1) X-ray shows severe periapical pathology around both the mesial and distal tooth roots. 2) Buccal fenestration around the mesial root following a vertical incision and flap. 3) The extracted mesial root with cyst removed. 4) The extraction site.
Endodontics root canal failure leading to extraction.
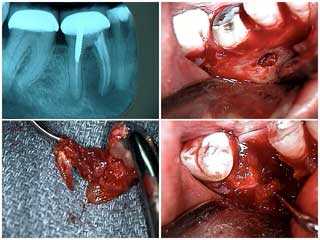
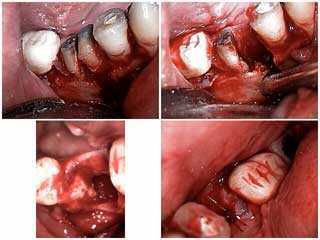
Extraction of a lower molar tooth due to severe periapical pathology. 1) Sectioning of the mesial and distal roots. 2) Removal of the mesial root. 3) & 4) The extraction site. The patient’s swollen jaw resolved very quickly.
Extraction of a lower molar tooth due to severe periapical pathology. 1) Sectioning of the mesial and distal roots. 2) Removal of the mesial root. 3) & 4) The extraction site. The patient’s swollen jaw resolved very quickly.
Endodontics root canal problems complications.
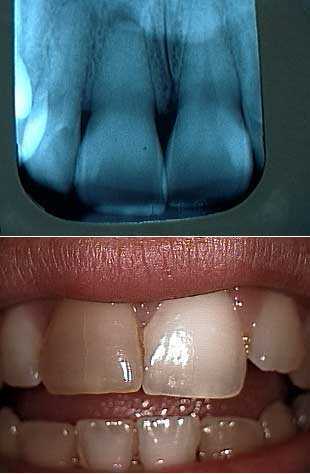
The upper right central incisor (on the left in this photo) shows complete obliteration of the root canal from calcification secondary to a history of trauma. Note discoloration of coronal portion of tooth. This is a result of the breakdown of blood in the pulpal chamber and the leaching of hemosiderin into the dentinal tubules.
The upper right central incisor (on the left in this photo) shows complete obliteration of the root canal from calcification secondary to a history of trauma. Note discoloration of coronal portion of tooth. This is a result of the breakdown of blood in the pulpal chamber and the leaching of hemosiderin into the dentinal tubules.
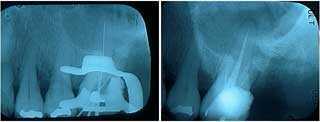
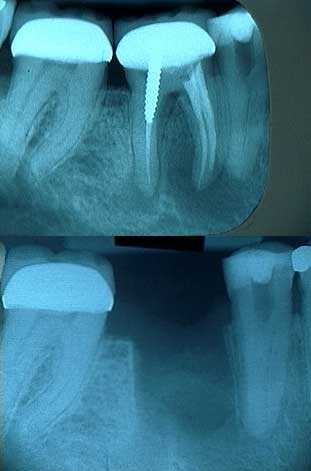
Endodontics root canal problems complications. X-rays of root canal therapy showing initial lengths and then final obturation in an upper left first molar. The root canal in this tooth showed calcification.
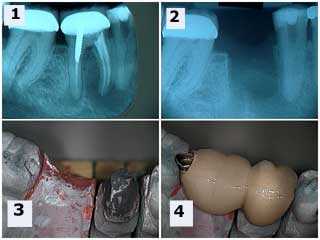
Endodontics root canal complications. Two teeth dental bridge with an occlusal rest seats onto the rest preparation in the mesial of the second molar dental crown. This eliminates the need for removing the second molar crown. The premolar did receive root canal therapy following healing of the extraction site.
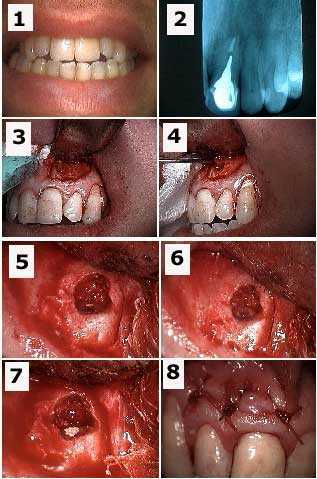
Endodontics root canal failure requiring oral surgery. Apicoectomy tooth #9 and retrograde filling to treat a failing root canal that resulted in a swollen upper lip. 1) Pre-op photo. 2) X-ray of tooth #9 with a cast post and root canal filled with gutta percha to the root apex. 3) Initial semilunar incision exposes the bony fenestration. 4) The cyst is being pulled through the osteotomy with a forceps. 5) Osseous preparation exposes the tooth root apex with the gutta percha visible. 6) Preparation into the root apex to make room for the retrograde filling. 7) Retrograde filling material (MTA, Mineral Trioxide Aggregate) placed into root apex preparation. 8) Sutures.
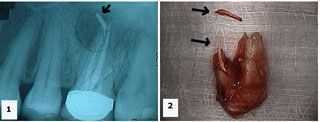
Endodontics root canal failure leading to a swollen jaw and tooth extraction. A hopeless tooth. 1) X-ray shows an upper first molar tooth with gutta percha extruded into a large radiolucent area. 2) Palatal photo of the extracted tooth shows the extent of the gutta percha extrusion. The extra fragment shown is also gutta percha.