Tooth Sensitivity – Tooth Pain – Sensitive Teeth
April 20, 2010 11:51 amTooth sensitivity and tooth pain can typically come from one or two places:
1.Nerves inside the tooth (in the pulp or root canal – they mean the same thing)
and/or
2.Nerves outside the tooth (in the surrounding gum and/or jawbone)
——————–
1. Nerves inside the tooth can become irritated from:
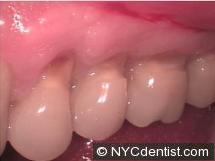
a.Gum recession – the loss of gum around the tooth exposes the tooth root which can be sensitive to air and liquid temperature changes.The sensitivity comes from within the undamaged tooth, not the gum.
b.Tooth erosion – frequently associated with gum recession, this also involves V-shaped notching in the tooth root.This is frequently a result from overly aggressive horizontal tooth brushing with a hard toothbrush that actually causes physical damage to the tooth.
Sensitivity to air and liquid temperature changes from tooth erosion comes from loss of tooth structure at the gum line.The sensitivity comes from within the damaged tooth, not the gum. A dentist may also recommend additional dentistry like bonding to cover the damaged tooth structure.
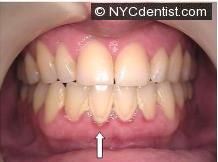
c.Tooth Decay (cavity, dental caries) – a dental cavity is a bacterial infection of a tooth.Sometimes infections cause sensitivity or pain.If you have a cut on your finger and it gets slightly infected, it can become quite sensitive.Infection within a tooth can also hurt.
Sensitivity to air and liquid temperature changes from a cavity comes from loss of tooth structure and the physical exposure of nerve endings within the tooth to the infection.The sensitivity comes from within the damaged tooth, not the gum.
If a cavity is relatively shallow, then a filling of various materials like Amalgam (silver) or Bonding (tooth-colored) may be used.If it is deep, then root canal therapy may also be needed. Obviously, the person in this photo needs help from a dentist.Don’t wait!
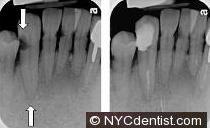
d.Root canal infection – the pulp (or root canal) of a tooth is the combined blood vessel and nerve that travels through the middle of a tooth much like an electrical wire travels through the middle of a wall in your home.
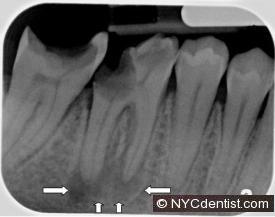
A deep cavity is shown touching the nerve space in the x-rays below. The white vertical line in the second x-ray shows the tooth after root canal therapy (and a temporary filling) have been placed.In this case the infection appears to have been largely contained within the tooth itself.
The tooth may have initially been sensitive in this example but pain can become quite severe in about half of these cases.The pain could result in the need for emergency care in either a dental office or hospital. The person in this photo needed help from an endodontist (root canal specialist). Don’t wait!
——————–
2. Nerves outside the tooth can become irritated from:
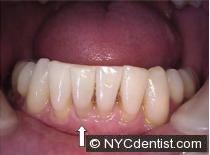
a.Gum disease – the gums are the soft tissue (skin) that covers the teeth and bones in your mouth.The presence of plaque (a bacterial infection on the outside of your tooth at the gum line) can cause gingivitis (an infection of the gum, or gingiva).
The white plaque can be seen around the lower teeth.It is surrounded by red, inflamed gums (gingivitis).The gums around these teeth can become sensitive.It may become more noticeable to women who are either pregnant or premenstrual since female hormones have a significant effect on the gums.The gums will probably also bleed when they are touched.If left untreated this can progress to more serious gum disease. It also gives you bad breath!
b.Root canal infection –
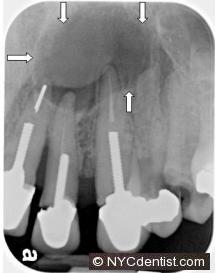
This root canal infection seems to have gone on for a longer period of time than the previous root canal example.Sensitivity may have occurred years earlier and then went away as the infected nerve died.The infection appears to be spreading into the surrounding jaw bone as seen by the dark circles around the tooth roots.This may result in swelling, in addition to pain, and could become a medical emergency.Facial swelling can become life threatening and is a frequent cause of tooth-related hospital emergency room visits. The person in this photo needs help from an endodontist (root canal specialist) and/or an oral surgeon at this point.
c.Cysts –
A cyst can develop in the jaw bone if an infection is left untreated.Again, the pain may have initially experienced sensitivity in this area and ignored it.The patient may still notice sensitivity if they press their finger high on their gum about where their tooth roots are located.A cyst can actually cause teeth to move.It can sometimes be the cause of a space developing between teeth in the same jaw.
d.Hyperocclusion or Drift –
Hyperocclusion results when teeth in opposing jaws bite against each other harder than they should.This can result from Supraeruption or Drift.
Supraeruption occurs when a tooth does not have an exact opposite tooth in the opposite jaw to bite against.Teeth will frequently continue to grow out of the gum until they either bite on the gum of the opposing jaw or hit a tooth in the opposing jaw off its vertical axis.
Drift occurs when a tooth tilts forward when another adjacent tooth in the same jaw is missing.When a tooth drifts forward, its back biting surface actually begins to bite harder against the teeth in the opposing jaw.
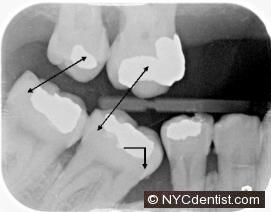
Hyperocclusion and Drift and be seen in the x-ray above.When combined with the presence of plaque the long term health of the teeth are severely compromised.The increased biting forces on these teeth, combined with the presence of hardened plaque, can cause sensitivity in both within the tooth and/or in the surrounding gums.
Periodontist (gum specialist) and orthodontist consultations should be sought.
e. Other reasons for teeth sensitivity – This can include TMJ-related symptoms, sinus infection, psychological and/or other medical illnesses.This may also need to be explored.
Tags: sensitive teeth, sensitive tooth, teeth hurt, teeth pain, teeth sensitive, teeth sensitivity, tooth hurts, tooth pain, tooth sensitive, Tooth SensitivityCategorised in: Dr. Dorfman Says
This post was written by Dr. Jeffrey Dorfman